Dysbiosis Allergic and Inflammatory Colitis Crohn’s Ulcerative IBS Leaky Gut Syndrome
CORE Protocols >>
Living Probiotics
Living Probiotic Ultra
GastroZyme
DigestEase
Cell Defense PLUS
GastroHeal
NutriDefense
ADVANCED Protocols >>
NutrImmune 26Y
IBS-Care
NutruSilver
AllicinMED
Nutriodine
Glutenase
———————————————————————————————————————————–
Ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease is characterized by recurrent attacks of diarrhea with mucus and blood, alternating with periods of calm. Symptomatology Symptomatology of ulcerative colitis is characterized by digestive and extradigestive manifestations.
Digestive manifestations are represented by diarrhea with blood, mucus and pus. Also may appear abdominal pain, tenesmus and abdominal cramps. Palpation of the abdomen is painful in hypogastrium or on colic trajectory. Diarrhea episodes usually occur in a total of 3 to 10 bloody stools per day, and in severe forms can occur only emission of blood, mucus and pus.
Extra-digestive manifestations are represented by anemia, secondary to blood loss, fever, weight loss and fatigue.
Other conditions that may occur simultaneously, but in connection with ulcerative colitis are:
Sclerosing colangite;
Liver disease;
Secondary amyloidosis;
Ankylosing spondylitis.

Paraclinical examination. Paraclinical explorations that help diagnose ulcerative colitis are biological investigations and investigations which highlights morphological changes. Laboratory tests appear altered in active periods of illness and are:
Iron deficiency anemia;
Hypoalbuminaemia;
ESR increased;
Increased C-reactive protein.
Endoscopy is useful in highlighting the damage. Typical of ulcerative colitis is affecting the rectum, but the continuous character of lesions which are seen at endoscopy. Therefore with a simple endoscopy, the diagnosis may be suggested and then confirmed by biopsy. The typical endoscopic appearance of mucosa is full of blood. The mucosa is friable with superficial ulcers, diffuse erythema and loss of vascular typical design. The mucosa is covered with pus and mucus. Colonoscopy is used to assess the degree of extension of ulcerative colitis in the colon. Biopsy of the colic mucosa is mandatory for diagnosis, assessing severity of injuries in this way. Positive diagnosis will put on the presence of diarrhea with blood, mucus and pus and also by the appearance of the colic mucosa seen at endoscopy, followed by confirmation, which is done by biopsy.
Classification ulcerative colitis is based on clinical forms, on the assessing of the severity of lesions and based on the localization of the lesions. Clinical forms of ulcerative colitis:
- Fulminant form of ulcerative colitis;
- Intermittent chronic form of ulcerative colitis, characterized by the occurrence of acute episodes on the background of almost complete remission;
- Chronic continuous form of ulcerative colitis, very rare.
The assessing of the severity of the lesions is done after Trulove’s classification, which is based on the number of stools and intensity of clinical signs:
- Mild form of ulcerative colitis: characterized by up to 4 stools / day with blood and mucus, and the patient’s general condition is good, without fever or denutrition and anemia is discreet;
- Medium form of ulcerative colitis: with 4-6 stools / day, anemia and low grade fever;
- Severe form of ulcerative colitis: more than 6 stools / day, high fever, anemia and hypoalbuminemia, blood in large amounts in stool and malaise.
After localization, ulcerative colitis is classified as follows:
- Proctitis, this form of injury occurs in the rectum or at rectosigmoid level;
- Left colitis, lesions affecting the entire descending colon;
- Pancolitis, lesions affecting the entire colon.
 Complications:
Complications:
- Toxic megacolon;
- Perforation with secondary peritonitis;
- Intestinal stenosis;
- Massive bleeding with severe anemia;
- Colon cancer.
Treatment Treatment begins with some dietary measures, by which should be avoided if possible milk and milk products, raw vegetables and fruits, especially those with seeds and concentrated sweets. Drug treatment depends on the intensity of the disease:
- In severe forms of ulcerative colitis, nutrition will be done parenteral, will begin fluid and electrolyte correction. Corticosteroid is administered in high doses for several weeks. After treatment with corticosteroids are administered 5-aminosalicylates acid or salazopirin. In toxic forms of disease will be administrated antibiotics;
- In mild forms of ulcerative colitis are administered 5-aminosalicylates acid or salazopirin.
 Surgery is rarely practiced, in case of perforation of the colon, in case of toxic megacolon or if the bleeding can not be controlled therapeutically.Development of colon cancer can occur in more than 10 years of disease, if is affected the entire colon and if severe epithelial dysplasia exist. Because of this, endoscopic surveillance is mandatory in patients with ulcerative colitis which has a long evolution.
Surgery is rarely practiced, in case of perforation of the colon, in case of toxic megacolon or if the bleeding can not be controlled therapeutically.Development of colon cancer can occur in more than 10 years of disease, if is affected the entire colon and if severe epithelial dysplasia exist. Because of this, endoscopic surveillance is mandatory in patients with ulcerative colitis which has a long evolution.
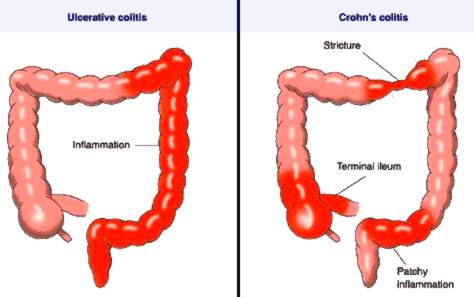

Crohn’s Disease Colitis >>
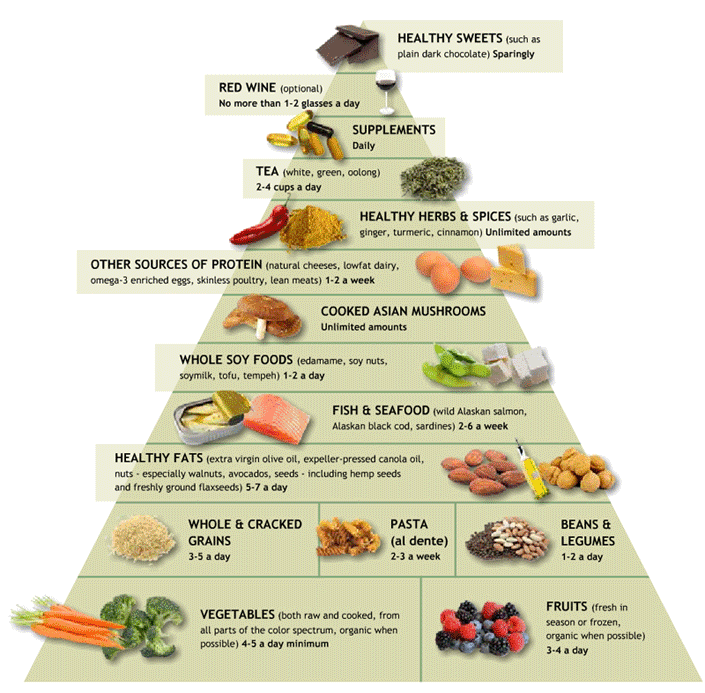
Healthy Diet Choice Pyramid for Colitis … Gluten Free, Lactose Free, GMO Free, and Processed Food Free +++






Antibiotics, hormones, and other drugs are given to chickens and cattle used for food. Stress, medications, and typical American diet all promote dysbiosis.




Disclaimer: These Wellness Protocols are not intended to replace the attention or advice of a physician or other qualified healthcare professional. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
